Bob Marley Spider: Facts About the Reggae-Inspired Arachnid
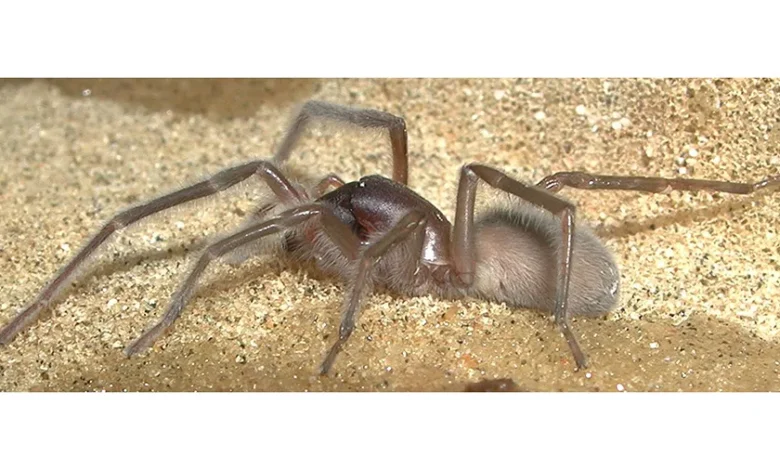

The natural world has always been full of surprises, but sometimes its wonders connect to human culture in unexpected ways. One such example is the Bob Marley Spider, a species scientifically known as Desis bobmarleyi. This spider, discovered relatively recently, carries not only fascinating biological traits but also a cultural connection to one of the most iconic musicians in history.
Naming new species after celebrities or cultural icons is a practice that scientists occasionally use to draw attention to discoveries, making them more memorable to the public. In the case of the Bob Marley Spider, its association with the legendary reggae musician instantly sparked curiosity and made headlines worldwide. After all, how often do you hear about a spider sharing its name with a global music icon?
The Bob Marley Spider is more than just a quirky name. It represents the adaptability and uniqueness of life on Earth, thriving in an unusual environment where few other spiders can survive. Its discovery not only added to scientific knowledge but also highlighted how biology and culture can intersect in unexpected and fascinating ways. In this article, we’ll explore its discovery, physical traits, behavior, and the deeper meaning behind its reggae-inspired name.
Discovery of the Bob Marley Spider
The Bob Marley Spider was first described in 2017 by a team of researchers studying intertidal spiders. Its scientific name, Desis bobmarleyi, belongs to a genus of spiders known for their unusual ability to survive in tidal zones. Found in the mangroves and coastal regions of Queensland, Australia, this spider’s discovery fascinated scientists because of its rare lifestyle and distinct habitat.
The decision to name the species after Bob Marley was more than a random choice. Researchers noted that the spider spends much of its life between high and low tides, a lifestyle that resonated with Marley’s song “High Tide or Low Tide.” By naming it in his honor, scientists not only paid tribute to Marley’s influence but also created a unique way to connect broader audiences to the wonders of biodiversity.
Naming new species after cultural figures is not uncommon. It often serves as a tool to engage the public and encourage interest in scientific research. In this case, associating a little-known marine spider with one of the world’s most beloved musicians helped bring global attention to an otherwise overlooked part of nature. The discovery also underscored how science can use creativity and culture to raise awareness of ecological diversity.
Scientific Classification and Features
The Bob Marley Spider belongs to the family Desidae and the genus Desis. Its full scientific name, Desis bobmarleyi, reflects both its taxonomic placement and its cultural homage. Members of this genus are known for their amphibious habits, which set them apart from most terrestrial spiders.
Physically, the spider is small to medium in size, with a body that is well-suited to its watery environment. Its coloration tends to be muted, blending with the mangrove roots, rocks, and sand that form its habitat. Unlike more flamboyant spiders, the Bob Marley Spider relies on camouflage for survival rather than bright markings or venomous displays.
What makes this spider truly unique is its ability to adapt to tidal changes. During high tide, it hides in air pockets within shells, barnacles, or plant debris, waiting for the waters to recede. This adaptation is rare among spiders, most of which are strictly land-dwelling creatures. Its amphibious traits make it an important subject of study for biologists interested in evolutionary adaptability.
The Bob Marley Spider may not be flashy or dangerous, but its distinct features and resilience make it stand out. Its biological quirks are as fascinating as the cultural story behind its name, giving it a unique place in the world of arachnology.
Habitat and Behavior
The Bob Marley Spider’s primary habitat is the intertidal zone—an environment shaped by the constant rise and fall of ocean tides. It has been observed in coastal mangroves and along sandy shores, areas where few spiders can thrive. These zones are challenging habitats because they alternate between being underwater during high tides and exposed during low tides.
To cope with this, the spider has developed remarkable behavioral adaptations. During high tide, it retreats into small crevices or hides inside empty shells and plant material, trapping air to create a safe breathing pocket. When the tide goes out, it emerges to hunt small invertebrates or scavenge for food along the exposed shore. This ability to survive in two drastically different conditions makes it one of the most adaptable spiders known.
Its presence in such ecosystems also highlights the importance of biodiversity in fragile coastal regions. Intertidal zones are critical to marine and terrestrial interactions, supporting species that bridge the gap between land and sea. The Bob Marley Spider plays a role in maintaining this balance, even if its influence is subtle. By feeding on small creatures, it helps regulate populations and contributes to the ecological web of its environment.
Studying the spider’s behavior has also provided insights into how life can adapt to extreme and fluctuating conditions. It serves as a reminder that even the smallest species have lessons to teach us about resilience and survival.
Cultural Significance of the Name
Naming the spider after Bob Marley was both symbolic and meaningful. Marley’s music, often inspired by themes of harmony, resilience, and nature, resonates with the spider’s lifestyle. The connection to his song “High Tide or Low Tide” perfectly reflects the spider’s existence in tidal zones. Scientists wanted to honor Marley’s cultural impact while also creating a memorable way to draw attention to biodiversity.
This isn’t the first time scientists have named species after celebrities. There are beetles named after Roy Orbison, fish honoring Frank Zappa, and even a fungus named after SpongeBob SquarePants. Such naming conventions might seem playful, but they serve a serious purpose: they make scientific discoveries more relatable and spark curiosity in people who may not otherwise engage with biology.
For fans of Bob Marley, the naming of the spider feels like a tribute that ties art and science together. Marley’s global influence goes beyond music; his values of peace, unity, and respect for nature continue to inspire generations. Associating his legacy with a resilient and unique creature like this spider is a fitting nod to his enduring impact.
Conservation and Scientific Importance
The Bob Marley Spider may not be endangered, but its habitat faces significant threats. Intertidal zones and mangrove forests are under pressure from climate change, pollution, and coastal development. Rising sea levels and habitat destruction could eventually impact the delicate ecosystems that support this and many other species.
Conservation of these habitats is crucial, not just for the Bob Marley Spider but for countless marine and terrestrial organisms. Protecting mangroves and coastal regions helps maintain biodiversity, prevent erosion, and support local communities. By spotlighting unique creatures like Desis bobmarleyi, scientists hope to raise awareness about the need to preserve such ecosystems.
Beyond conservation, the spider’s unique adaptations make it an important subject for research. Studying how it survives in intertidal zones can shed light on evolutionary processes and inspire innovations in biology and environmental science. Its resilience offers valuable lessons about survival in fluctuating environments—knowledge that may prove essential as ecosystems worldwide face increasing instability.
By blending cultural significance with scientific discovery, the Bob Marley Spider has become more than just an arachnid. It stands as a symbol of how nature and human creativity can intersect to highlight the importance of protecting life in all its forms.
Conclusion
The Bob Marley Spider is a remarkable reminder of how science and culture can intertwine in unexpected ways. Discovered in the tidal zones of Australia, this small but resilient spider thrives in one of nature’s most challenging habitats. Its amphibious lifestyle, unique adaptations, and cultural tribute to Bob Marley make it one of the most fascinating species named in recent years.
By naming it after the reggae legend, scientists not only honored Marley’s global influence but also created a bridge between ecological discovery and cultural storytelling. This connection helps raise awareness about biodiversity, conservation, and the fragile beauty of intertidal ecosystems.
Ultimately, the Bob Marley Spider teaches us about resilience—whether it’s surviving high tide or low tide, or finding harmony between human culture and natural life. It is both a scientific curiosity and a cultural tribute, ensuring that Bob Marley’s spirit lives on not only in music but also in the world of natural wonders.
FAQs About the Bob Marley Spider
What is the Bob Marley Spider’s scientific name?
The spider is scientifically known as Desis bobmarleyi.
Where was the Bob Marley Spider discovered?
It was discovered in the coastal intertidal zones of Queensland, Australia.
Why was the spider named after Bob Marley?
The name honors Bob Marley, inspired by his song “High Tide or Low Tide,” which reflects the spider’s tidal habitat.
What makes the Bob Marley Spider unique compared to other spiders?
Its ability to live in intertidal zones, hiding underwater in air pockets during high tide and emerging to hunt at low tide.
Is the Bob Marley Spider dangerous to humans?
No, it is not considered dangerous to humans.
What type of habitat does the Bob Marley Spider prefer?
It thrives in mangroves, sandy shores, and intertidal coastal environments.
Are there other species named after musicians like Bob Marley?
Yes, many species are named after celebrities, such as a beetle named after Roy Orbison and fish honoring Frank Zappa.
Is the Bob Marley Spider endangered?
It is not currently endangered, but its habitat faces threats from climate change and coastal development.
You May Also Read: Rosebury Farm




