Fluorescent Tubes: Types, Uses, and Energy Efficiency Guide
Fluorescent tubes have been a cornerstone of modern lighting for decades, offering efficient and versatile illumination for homes, offices, and industrial environments. Known for their energy-saving properties and long lifespan, fluorescent tubes remain a popular choice despite the rise of LED lighting technology. Understanding the various types, applications, and maintenance requirements of fluorescent tubes is essential for anyone looking to maximize their lighting performance and efficiency.
Fluorescent lighting is widely appreciated for its ability to provide bright, even illumination while consuming less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs. It is commonly used in environments that require consistent and widespread lighting, such as offices, factories, schools, and commercial spaces. Moreover, specialized fluorescent’tubes, including UV and germicidal lamps, extend their application beyond simple illumination to areas like laboratories, medical facilities, and signage.
This guide explores the fundamentals of fluorescent tubes, including their types, installation processes, maintenance tips, and energy considerations. By understanding these factors, readers can make informed decisions about selecting the right fluorescent lighting for different settings. Whether you are a homeowner seeking reliable lighting or a business owner aiming to reduce energy costs, this article provides a comprehensive overview to help you harness the full potential of fluorescent tubes.
What Are Fluorescent Tubes?
Fluorescent tubes are a type of gas-discharge lamp that produces light through the excitation of mercury vapor inside the tube. When electricity passes through the tube, it excites the mercury atoms, emitting ultraviolet (UV) light. This UV light interacts with the phosphor coating on the inside of the tube, producing visible light. This process is highly efficient, allowing fluorescent’tubes to generate more light per watt than traditional incandescent bulbs.
Developed in the early 20th century, fluorescent lighting revolutionized interior illumination by providing consistent, bright, and energy-efficient lighting. Over time, advances in technology have led to improved phosphor coatings, more reliable ballasts, and the introduction of compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs) for residential and portable applications. Unlike incandescent bulbs, which produce light through heating a filament, fluorescent tubes rely on a chemical and electrical process, resulting in lower energy consumption and less heat emission.
Fluorescent tubes typically consist of a cylindrical glass tube filled with low-pressure mercury vapor, electrodes at both ends, and a phosphor coating on the inner surface. The combination of these components ensures a steady and bright output suitable for a variety of lighting applications. Compared to LEDs and incandescent bulbs, fluorescent tubes provide excellent color rendering and coverage for larger spaces, making them ideal for offices, industrial facilities, and classrooms where uniform lighting is essential.
Types of Fluorescent Tubes
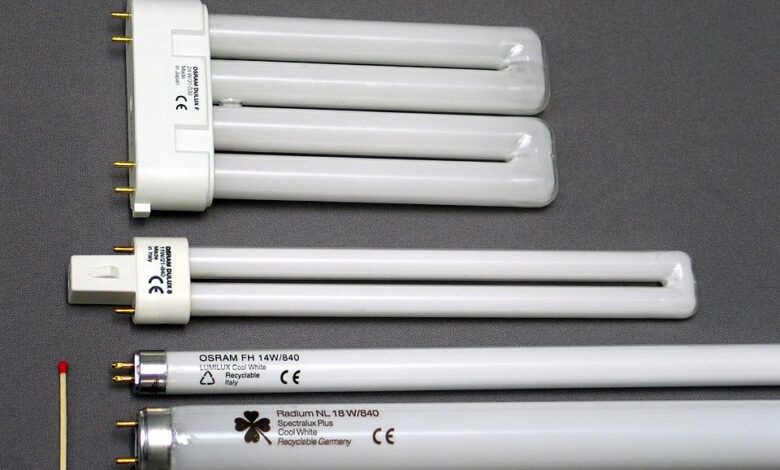
Fluorescent tubes come in several types, each tailored to specific lighting needs. The most common linear tubes are T5, T8, and T12, distinguished by their diameter and wattage. T5 tubes are thin, energy-efficient, and often used in modern office environments. T8 tubes are slightly larger and are the most widely used due to their balance between cost and efficiency. T12 tubes are older, thicker, and less energy-efficient but are still found in older installations.
Compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs) are another popular type, designed for residential or small-scale applications. CFLs offer energy efficiency and portability while fitting into standard light fixtures. They are ideal for kitchens, garages, and bedrooms, providing bright illumination without consuming excessive electricity. Additionally, CFLs are available in various color temperatures, allowing for warm or cool lighting according to preference.
Specialty fluorescent tubes, such as UV and germicidal lamps, serve niche applications. UV fluorescent tubes are used for disinfection, laboratory work, and aquariums, while color-rendering fluorescent’tubes enhance visual accuracy in retail displays or art studios. The choice of tube type depends on factors such as energy efficiency, application, brightness, and desired color temperature. Understanding these differences ensures that the selected fluorescent tube meets both functional and aesthetic requirements.
Uses and Applications
Fluorescent tubes are widely used in commercial and industrial settings due to their ability to provide uniform, bright illumination across large areas. Offices, warehouses, factories, and schools commonly rely on T8 and T5 tubes for consistent lighting, enabling productive and safe environments. Their energy efficiency helps reduce electricity bills, particularly in spaces where lights remain on for extended periods.
In residential applications, fluorescent tubes and CFLs are ideal for kitchens, basements, garages, and utility rooms. Their bright, clear light makes tasks like cooking, cleaning, and DIY projects easier while consuming less energy than incandescent bulbs. Additionally, compact fluorescent lamps can be used in table lamps or ceiling fixtures, offering flexibility in home lighting design.
Specialized applications include laboratories, hospitals, and signage. Germicidal fluorescent tubes help sterilize equipment and water, while high-color-rendering tubes improve visibility in retail and design settings. Fluorescent’tubes also find use in growing plants indoors, aquarium lighting, and other controlled environments where specific light wavelengths are beneficial. Their versatility and range of sizes make fluorescent tubes suitable for virtually any lighting scenario requiring efficient, reliable illumination.
Installation and Maintenance Tips
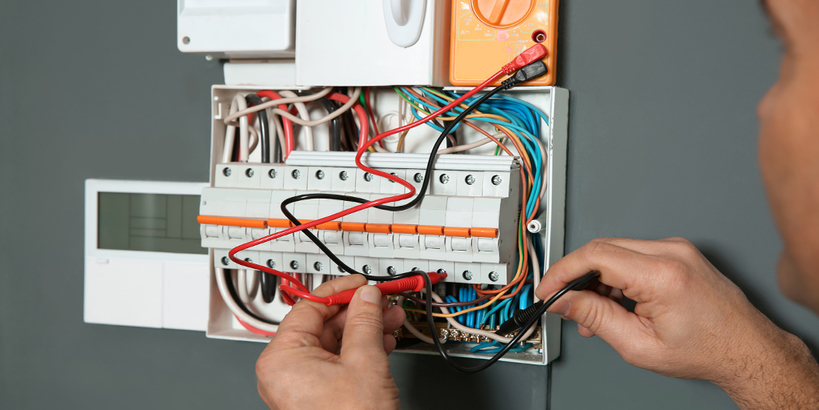
Proper installation of fluorescent tubes is critical for safety and performance. Always ensure the power is turned off before replacing or installing tubes. Linear fluorescent tubes typically require a fixture with a compatible ballast, while CFLs can be screwed directly into standard sockets. Align the tube pins with the fixture sockets and rotate carefully until securely seated. Following manufacturer instructions ensures correct installation and prevents damage to the tube or fixture.
Maintenance is equally important for longevity and performance. Common issues include flickering, dimming, or failure to start, often caused by aging ballasts, loose connections, or worn electrodes. Regularly inspecting the fixture and replacing faulty components can prevent these problems. Cleaning the tubes periodically removes dust that can reduce brightness and efficiency.
Replacing tubes at the first sign of dimming or flickering helps maintain consistent illumination. For large-scale installations, it’s advisable to replace all tubes simultaneously to ensure uniform brightness. Using energy-efficient ballasts and high-quality tubes also contributes to longer lifespan and reduced maintenance costs. Proper handling and disposal, especially due to the mercury content in fluorescent tubes, are crucial to minimize environmental impact and comply with safety regulations.
Energy Efficiency and Environmental Considerations
Fluorescent tubes are significantly more energy-efficient than incandescent bulbs, consuming up to 75% less electricity while producing comparable light output. Their long lifespan, often ranging from 7,000 to 20,000 hours depending on type and usage, further enhances cost-effectiveness. Energy savings make fluorescent tubes an attractive option for businesses and households seeking to reduce utility bills without sacrificing illumination quality.
However, environmental considerations are important due to the mercury content in fluorescent tubes. Mercury is a hazardous substance that requires careful handling, proper recycling, and adherence to local disposal regulations. Many countries have established recycling programs to safely process spent fluorescent tubes, recovering valuable materials and preventing environmental contamination.
In comparison with modern LED lighting, fluorescent tubes are less energy-efficient but still offer advantages in certain applications, especially where bright, widespread lighting is needed. By selecting the appropriate tube type, using energy-saving ballasts, and following proper disposal protocols, users can enjoy the benefits of fluorescent lighting while minimizing environmental impact.
Conclusion
Fluorescent tubes remain a reliable and versatile lighting solution, offering energy efficiency, long lifespan, and bright, uniform illumination for a wide range of applications. From commercial and industrial spaces to residential and specialized environments, understanding the different types, installation methods, and maintenance practices ensures optimal performance.
By selecting the right fluorescent tube, maintaining it properly, and considering energy and environmental factors, users can maximize both the functional and economic benefits of fluorescent lighting. Whether upgrading an office, retrofitting a home, or installing specialty lighting, fluorescent tubes provide a dependable and efficient solution for effective illumination.
FAQs
What is the difference between T5, T8, and T12 fluorescent tubes?
T5 tubes are thin and energy-efficient, T8 tubes are widely used for general applications, and T12 tubes are older, thicker, and less efficient.
How long do fluorescent tubes typically last?
Lifespan ranges from 7,000 to 20,000 hours, depending on type, usage, and ballast quality.
Can fluorescent tubes be recycled safely?
Yes, many recycling programs handle fluorescent tubes due to their mercury content. Proper disposal prevents environmental contamination.
Why do fluorescent tubes flicker or fail prematurely?
Common causes include worn electrodes, faulty ballasts, loose connections, or improper installation.
Are fluorescent tubes more energy-efficient than incandescent bulbs?
Yes, they consume up to 75% less electricity while providing comparable illumination.
Can fluorescent tubes be used outdoors?
Yes, but they should be in weatherproof fixtures to protect against moisture and environmental damage.
How do I choose the right color temperature for my fluorescent tube?
Consider the application: cool white for offices or industrial areas, warm white for residential or cozy spaces.
You May Also Read: Exmouth Tide Times