iwconfig Fedora: How to Configure Wireless Networks on Fedora Linux
Managing wireless networks on Fedora Linux can be both exciting and challenging, especially for users who prefer command-line tools. One of the most essential utilities for wireless management is iwconfig Fedora, a command-line tool that allows you to view, configure, and troubleshoot wireless network interfaces. Unlike GUI-based network managers, iwconfig Fedora provides granular control over wireless parameters, making it invaluable for IT professionals, system administrators, and Linux enthusiasts who need precise information and configuration options.
Understanding how iwconfig Fedora works is crucial for maintaining optimal connectivity. The tool enables users to set or change network parameters such as SSID, frequency, mode, and encryption keys. It also allows monitoring of key metrics like signal strength, link quality, and transmission power. This command-line approach is particularly useful in scenarios where GUI tools are unavailable, when troubleshooting network issues, or when working on remote servers. By mastering iwconfig Fedora, users can gain a deeper understanding of their network environment and quickly resolve common wireless connectivity problems.
In this guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about iwconfig Fedora, from basic usage and interface management to advanced configuration and troubleshooting techniques. We will also cover best practices for using this tool efficiently alongside other network utilities. By the end of this article, you’ll be able to confidently use iwconfig Fedora to configure, monitor, and optimize your Fedora wireless connections, whether for personal use or professional IT management.
Understanding iwconfig Fedora
What is iwconfig Fedora?
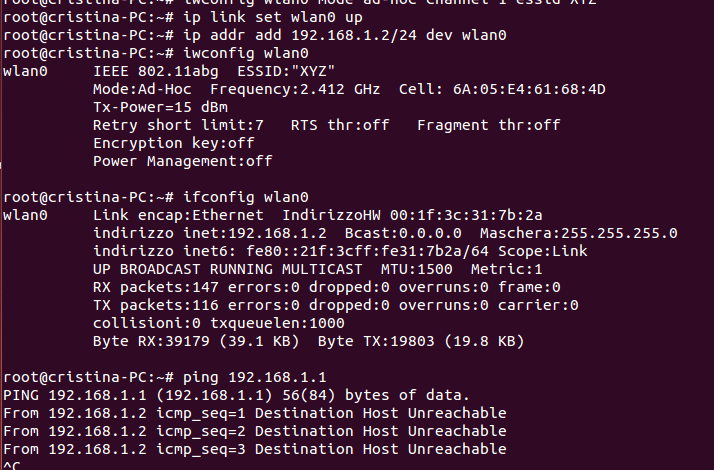
iwconfig Fedora is a command-line utility in Linux specifically designed for managing wireless network interfaces. While ifconfig is primarily used for wired network interfaces, iwconfig Fedora provides functionality tailored to wireless connections. With iwconfig Fedora, you can view the status of your wireless interfaces, connect to networks, and adjust important parameters such as the SSID, mode, channel, and encryption key.
One key advantage of iwconfig Fedora is its ability to provide detailed metrics that GUI-based network tools often obscure. For example, iwconfig Fedorag shows real-time values for signal quality, link quality, and noise levels, which can be essential for diagnosing weak or unstable connections. Additionally, it enables fine-grained control over wireless modes, allowing you to switch between managed, ad-hoc, or monitor modes depending on your needs. This level of detail makes iwconfig a powerful tool for users who require precise control over their wireless network environment.
Furthermore, iwconfig Fedora supports both temporary and persistent changes, giving users flexibility in testing new network settings without permanently altering configurations. It’s lightweight, widely available on most Linux distributions, and a staple in the toolkit of anyone managing wireless networks on Fedora.
Key Features and Functions
iwconfig Fedora offers a range of features that extend beyond basic connectivity. Users can configure the SSID to connect to specific networks, set encryption keys for secure access, and adjust parameters like transmission power to optimize network performance. It also allows monitoring of critical metrics such as link quality, signal strength, and bit rate, which are crucial for identifying issues like interference or weak connections.
Advanced users can leverage iwconfig Fedora to change wireless modes. Managed mode is standard for connecting to access points, ad-hoc mode enables peer-to-peer networking, and monitor mode allows capturing packets for network analysis. By understanding these modes, users can adapt their network setup to specific requirements, whether for secure office environments, troubleshooting scenarios, or advanced networking experiments.
Overall, the versatility and precision of iwconfig make it an indispensable tool for Fedora users who want to optimize their wireless experience. From routine monitoring to complex configuration, mastering its functions is key to efficient network management.
How to Use iwconfig on Fedora
Checking Wireless Interfaces
Before configuring a wireless network, it’s important to identify available interfaces. Using the command iwconfig without parameters lists all wireless interfaces along with their current settings. Common interface names include wlan0 or wlp2s0, depending on the Fedora version and hardware configuration.
Understanding these interface names is crucial because commands need to target the correct interface for configuration or troubleshooting. For instance, attempting to connect to a network using the wrong interface will fail. Additionally, iwconfig output provides real-time status of each interface, such as whether it is associated with an access point or its signal strength. This information is invaluable when diagnosing connectivity issues or checking network performance.
Connecting to a Wi-Fi Network
Connecting to a network with iwconfig requires specifying the SSID and, if necessary, the encryption key. For open networks, simply setting the SSID may be sufficient. For secured networks, WEP or WPA keys must be entered correctly. The process typically involves using commands like iwconfig [interface] essid [network_name] and iwconfig [interface] key [password].
It’s important to note that WPA/WPA2 networks often require additional tools, such as wpa_supplicant, alongside iwconfig to manage authentication. However, iwconfig remains useful for basic connection testing, monitoring, and temporary manual network configuration. By practicing these commands, Fedora users can gain confidence in connecting to networks without relying on GUI tools.
Monitoring Wireless Status
iwconfig provides detailed metrics that help monitor network health. Key values include signal strength, link quality, noise levels, and transmission power. These metrics allow users to identify issues like weak signals, interference, or potential hardware problems. Monitoring these parameters is essential for troubleshooting dropped connections, unstable performance, or low throughput.
By regularly checking these metrics, users can optimize network placement, adjust channels to reduce interference, and ensure that their wireless setup maintains a stable and fast connection. Combining iwconfig with tools like nmcli or ping can further enhance network monitoring and troubleshooting.
Advanced Configuration
Advanced Fedora users can use iwconfig to switch wireless modes, adjust transmission power, or configure custom parameters for specialized network setups. Managed mode connects to access points, ad-hoc mode enables device-to-device networking, and monitor mode supports packet capturing for analysis. Adjusting Tx-Power can improve signal range in challenging environments.
These advanced options provide the flexibility to optimize wireless performance, enhance security, and support complex network tasks. Mastery of these configurations distinguishes basic users from proficient Linux network administrators.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with iwconfig
Interface Not Found
If iwconfig fails to detect a wireless interface, the issue often lies in driver problems, disabled interfaces, or hardware recognition failures. Commands like ip link or lspci can help identify available hardware. Ensuring the correct driver installation and enabling the interface via ifconfig [interface] up or ip link set [interface] up usually resolves this problem.
Weak Signal or Dropped Connections
Weak or unstable signals can result from interference, poor placement, or channel conflicts. Using iwconfig to monitor signal strength and link quality allows users to adjust router placement, select optimal channels, or fine-tune transmission power. Regular monitoring ensures consistent connectivity and performance.
Authentication Problems
Authentication failures often stem from incorrect SSID entries, wrong encryption keys, or unsupported security protocols. Users should verify their network credentials and, when necessary, integrate wpa_supplicant with iwconfig for WPA/WPA2 networks. Proper configuration ensures secure and reliable connections.
Best Practices for Using iwconfig on Fedora
- Update Drivers: Keeping wireless drivers and firmware current enhances compatibility and performance.
- Use Root Permissions: Many configuration commands require sudo or root access.
- Document Settings: Record recurring network configurations for efficiency.
- Combine Tools: Use iwconfig alongside GUI tools and utilities like nmcli for a balanced approach.
Following these practices ensures stable, secure, and optimized wireless connectivity on Fedora Linux.
Conclusion
iwconfig remains an essential command-line tool for Fedora wireless network management, providing control, precision, and troubleshooting capabilities unmatched by GUI utilities. From identifying interfaces and connecting to networks to monitoring signal strength and adjusting advanced parameters, mastering iwconfig equips Fedora users with the skills to maintain stable, high-performance wireless connections.
By understanding its commands, metrics, and best practices, both beginners and advanced users can leverage iwconfig to optimize their wireless experience. Whether for personal use, professional IT management, or network troubleshooting, iwconfig Fedora empowers users with the knowledge and tools to control their wireless environment effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is iwconfig used for in Fedora Linux?
A command-line tool to configure and monitor wireless network interfaces.
How is iwconfig different from ifconfig?
ifconfig is for wired network interfaces, while iwconfig is specifically for wireless.
Can iwconfig connect to WPA2 networks?
Yes, but usually requires integration with wpa_supplicant for authentication.
How do I find my wireless interface name on Fedora?
Use iwconfig or ip link to list active interfaces.
What do the different iwconfig metrics mean (Tx-Power, Link Quality, Noise)?
Tx-Power indicates transmission strength, Link Quality shows connection stability, and Noise measures interference levels.
Why isn’t my wireless interface showing up in iwconfig?
Possible causes include driver issues, disabled interfaces, or unrecognized hardware.
Can I use iwconfig without root privileges?
Viewing metrics is possible, but changing configurations often requires sudo or root access.
How do I troubleshoot weak Wi-Fi signals using iwconfig?
Monitor signal strength, adjust Tx-Power, change channels, and optimize router placement.
Is iwconfig still relevant with modern Fedora NetworkManager tools?
Yes, it provides granular control and is invaluable for troubleshooting when GUI tools fail.
How can I permanently save iwconfig settings on Fedora?
By creating network configuration scripts or integrating settings with NetworkManager.
You May Also Read: Beat Airbrush