Rowing Machine: The Ultimate Guide to Home Workouts
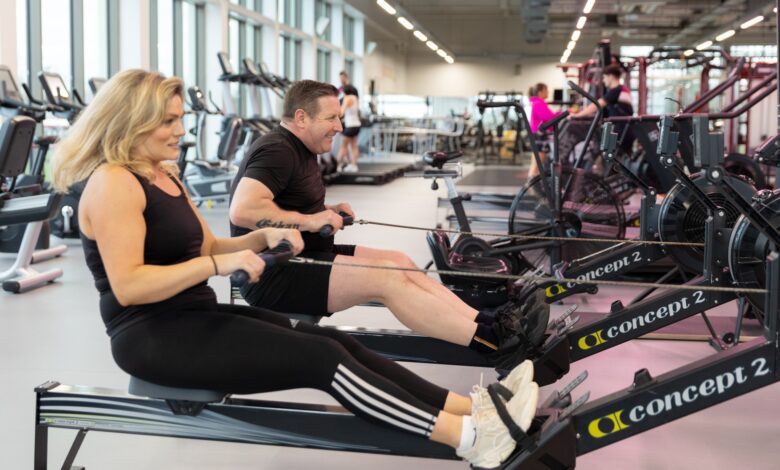

The rowing machine has emerged as one of the most versatile and effective fitness tools for home and gym workouts alike. Known for providing a full-body workout while being gentle on the joints, it has become increasingly popular among fitness enthusiasts of all levels. Unlike other cardio machines, a rowing machine engages multiple muscle groups simultaneously, including the legs, core, back, and arms, making it ideal for strength and endurance training. Beyond the physical benefits, rowing offers mental advantages such as stress reduction and improved focus, making it a holistic exercise option.
For beginners, rowing machines might seem intimidating, but with the proper technique and understanding of their functionality, anyone can incorporate them into their fitness routine. This guide aims to cover everything a user needs to know, from types of rowing machines and proper form to workout plans, benefits, and maintenance tips. By the end of this article, readers will have the knowledge to select the right rowing machine, perform exercises safely, and achieve measurable results.
Rowing machines are also highly adaptable to different fitness goals. Whether someone is looking to lose weight, build strength, improve cardiovascular health, or train for competitive rowing, these machines provide a scalable solution. Their compact designs, especially models suited for home use, allow users to enjoy high-quality workouts without the need for a full gym setup. This combination of efficiency, versatility, and accessibility makes the rowing machine an indispensable piece of fitness equipment in 2026.
History and Evolution of Rowing Machines
Rowing machines, also known as ergometers, have a long-standing history dating back to the 19th century. Originally developed for training professional rowers, these machines allowed athletes to simulate rowing movements indoors, regardless of weather or water conditions. Early models were often mechanical and simplistic, focusing primarily on technique and basic endurance training rather than full-body fitness.
Over time, rowing machines evolved to include multiple resistance types, significantly enhancing their versatility. Water resistance rowers replicate the feel of rowing on open water by using a water-filled flywheel, providing a smooth and natural rowing experience. Air resistance models generate resistance via a fan, allowing for scalable intensity based on the user’s effort. Magnetic rowers introduced quiet operation and adjustable resistance levels, making them popular for home use, while hydraulic rowers offered compact designs suitable for limited spaces.
In modern times, technology has further transformed rowing machines. Digital monitors, programmable workouts, and connectivity with fitness apps allow users to track performance, monitor heart rate, and set precise training goals. These advancements have broadened the appeal of rowing machines, transforming them from a niche training tool for competitive rowers into a mainstream fitness essential suitable for diverse exercise routines.
Types of Rowing Machines
Choosing the right rowing machine depends on fitness goals, space, and budget. Water rowers are praised for their smooth motion and realistic rowing experience. They are often constructed with wooden frames and water-filled flywheels, which mimic the natural resistance of rowing on a lake or river. The sound of water splashing adds to the immersive experience, making workouts enjoyable and motivating.
Air rowers use a fan mechanism to generate resistance. The harder a user pulls, the greater the resistance, allowing for high-intensity training and interval workouts. These rowers are durable and excellent for building cardiovascular endurance, making them popular in gyms and athletic training programs.
Magnetic rowers operate with magnetic resistance, offering silent operation and adjustable intensity levels. They are ideal for home settings, especially apartments or shared spaces where noise could be a concern. These machines often include digital displays and preset programs, providing users with a controlled and consistent workout experience.
Hydraulic rowers are the most compact and portable. They use pistons to create resistance and are suited for small spaces, though they may not provide the same fluid motion as water or air rowers. While less common among professional athletes, they are a practical option for beginners or casual users seeking convenience and affordability. Understanding the pros and cons of each type ensures users choose a machine that aligns with their needs and fitness ambitions.
Benefits of Using a Rowing Machine
One of the main advantages of rowing machines is their ability to provide a full-body workout. Every stroke engages major muscle groups, including the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, core, back, and arms. This simultaneous engagement helps build strength, enhance muscle tone, and improve overall fitness efficiently. Unlike isolated exercises, rowing trains the body in a functional and coordinated manner.
Rowing also offers significant cardiovascular benefits. Consistent use can increase heart rate, improve lung capacity, and boost endurance. It is an effective calorie-burning exercise, making it suitable for weight management or fat loss. Users can adjust the intensity to match their fitness level, ensuring workouts are challenging yet manageable.
A standout feature of rowing is its low-impact nature. Unlike running or jumping exercises, rowing minimizes stress on joints while still delivering a high-intensity workout. This makes it ideal for individuals recovering from injuries, older adults, or anyone seeking a joint-friendly cardio alternative.
Mental health benefits are another reason rowing is gaining popularity. The rhythmic motion and focus required during each stroke can reduce stress, enhance concentration, and promote a sense of calm. Many users report a meditative quality in rowing sessions, helping to relieve tension while improving physical fitness.
Proper Technique and Form
Correct technique is critical for maximizing benefits and preventing injury. A rowing stroke consists of four phases: catch, drive, finish, and recovery. The catch is the starting position, where the knees are bent, arms extended, and the body slightly leaned forward. During the drive, legs push against the footplate while the back and arms pull the handle toward the torso. The finish is the end of the stroke with legs extended and handle near the chest, and the recovery is the controlled return to the catch position.
Common mistakes include overusing the arms, rounding the back, or rushing the recovery phase. These errors reduce efficiency and may lead to back strain or muscle fatigue. Users should focus on leg drive first, followed by core engagement and arm pulling. Smooth, controlled movements optimize energy use and target muscles effectively.
Maintaining proper posture is essential. Engaging the core, keeping the back straight, and avoiding slouching enhances both performance and safety. Using mirrors or recording sessions can help monitor form, while professional guidance or instructional videos can accelerate learning. Over time, mastering proper technique maximizes calorie burn, improves muscle engagement, and ensures long-term sustainability of rowing workouts.
Rowing Machine Workouts and Training Plans
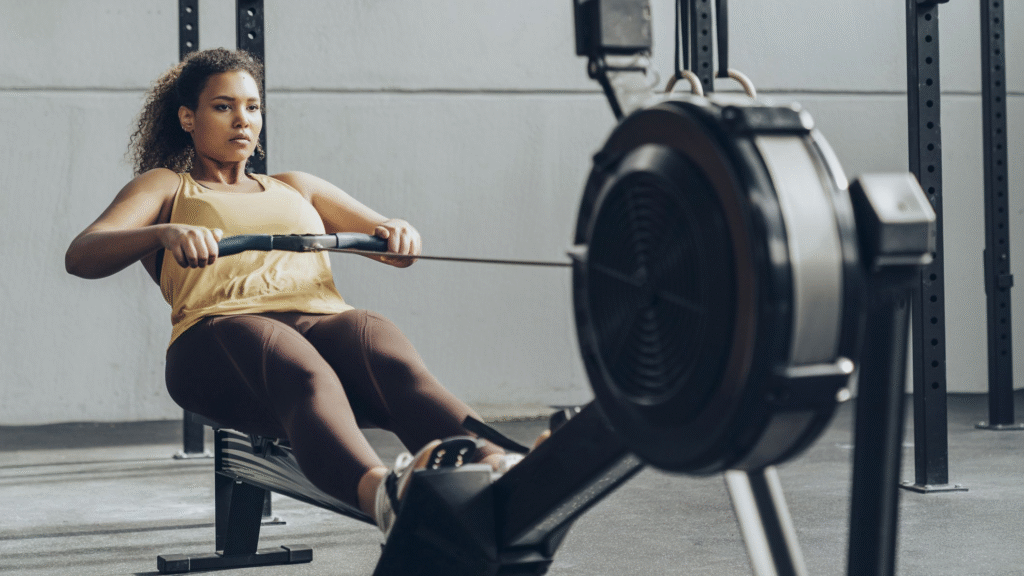
Rowing workouts can be tailored to all fitness levels. Beginners may start with 10-15 minute sessions focusing on form, gradually increasing duration and intensity. Shorter, consistent sessions help build endurance without overwhelming the body.
Intermediate users can incorporate interval training and resistance variations to challenge cardiovascular capacity and strength. Programs combining high-intensity sprints with recovery periods increase calorie burn and improve stamina.
Advanced athletes often perform long-distance sessions, time trials, or targeted training programs aimed at performance goals, such as increasing rowing speed or power output. Combining rowing with strength and flexibility exercises creates a balanced fitness plan.
Rowing is highly adaptable and can complement other workouts, including running, cycling, or weight training. By structuring workouts according to fitness level, users can progressively improve performance, prevent plateaus, and maintain motivation.
Choosing the Right Rowing Machine
Selecting the ideal rowing machine involves considering space, budget, resistance type, and user goals. Water rowers provide realistic rowing motion but may require more space. Magnetic rowers are compact and quiet, suitable for apartments. Air rowers are ideal for high-intensity training, while hydraulic models are budget-friendly and portable.
Top brands include Concept2, WaterRower, NordicTrack, and Stamina, each offering models with specific features like digital monitors, adjustable resistance, or foldable designs. Evaluating features, testing machines in-store, or reading reviews online can ensure a satisfying purchase. Aligning machine type with intended use, space constraints, and budget maximizes workout effectiveness.
Maintenance and Care
Proper maintenance ensures longevity and performance. Regularly clean rails, seats, and handles, and inspect moving parts and resistance mechanisms for wear. Lubricate rails or chains as recommended by the manufacturer, and replace worn parts promptly.
Safety during use and storage is critical. Ensure machines are stable, foot straps are secure, and monitor any unusual noises. Proper maintenance enhances safety, reduces repair costs, and keeps workouts consistent over time.
Conclusion
Rowing machines are versatile, effective, and low-impact tools for achieving full-body fitness, weight management, and cardiovascular endurance. By understanding the types of machines, mastering proper form, following structured workouts, and maintaining equipment, users can enjoy safe and efficient training. Whether for beginners or advanced athletes, integrating rowing into a regular fitness routine provides both physical and mental benefits, making it a highly valuable addition to any home or gym setup.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the best type of rowing machine for beginners?
Magnetic or hydraulic rowers are generally recommended due to quiet operation and easy resistance adjustment.
How many calories can I burn on a rowing machine per session?
Depending on intensity and duration, users can burn between 400–800 calories per hour.
Is rowing machine exercise good for weight loss?
Yes, rowing combines cardio and strength, making it highly effective for calorie burning and fat reduction.
Can rowing machines help build muscle as well as improve cardio?
Absolutely; rowing engages legs, core, back, and arms, providing both strength and endurance benefits.
How do I maintain my rowing machine for long-term use?
Regularly clean, lubricate moving parts, and inspect for wear to ensure smooth performance.
What are the most common mistakes to avoid while rowing?
Using improper form, over-relying on arms, slouching, and rushing recovery phases.
How often should I use a rowing machine for best results?
3–5 sessions per week is effective, depending on fitness level and goals.
Are rowing machines suitable for people with joint issues?
Yes, rowing is low-impact, making it gentle on knees, hips, and ankles.
How does a water rower compare to a magnetic or air rower?
Water rowers provide a realistic rowing feel, air rowers scale intensity with effort, and magnetic rowers are quiet and adjustable.
Can I do a full-body workout using only a rowing machine?
Yes, rowing targets major muscle groups while providing cardiovascular conditioning.
You May Also Read: Top 5 Websites to Find COS Discounts



